Blue poison dart frog
Dendrobates tinctorius ”azureus”

Black spots as fingerprints
The blue poison dart frog is a subspecies of the dyeing poison dart frog. The dyeing poison dart frog is one of the most varied species of poison dart frogs, and comes in a huge range of colours and patterns. The name dyeing poison dart frog comes from the fact that groups of indigenous people in areas where the frog lives, probably used the frog’s poisonous secretions to dye parrot feathers for decoration.
The blue poison dart frog inhabits rivers, lakes and ponds in South America. The frog has a sharp bluish colour with black spots that signal to predators that the frog is poisonous. The black spots are unique to each individual frog, a bit like human fingerprints.
The spotted pattern are unique for every frog - almost like the fingerprints of humans.
Photo: Uwe-Nassal-CC-BY-SA
The amount of black, blue, yellow and white varies in different groups of dyeing poison dart frogs.
Photo: H.-Zell-CC-BY-SA
The amount of black, blue, yellow and white varies in different groups of dyeing poison dart frogs.
Photo: H.-Zell-CC-BY-SA
The amount of black, blue, yellow and white varies in different groups of dyeing poison dart frogs.
Photo: Simon-Evans-CC-BY-SA
Poison from insects
The poison of the poison dart frog is produced by it feeding on certain insects that have toxic chemicals in their bodies. The venom from the insects stays in the frog’s body, and collects in glands. The frog can then release a toxic secretion from its skin whenever it feels threatened. Captive-bred blue poison dart frogs are not poisonous, as they are fed insects that are not carrying toxins.
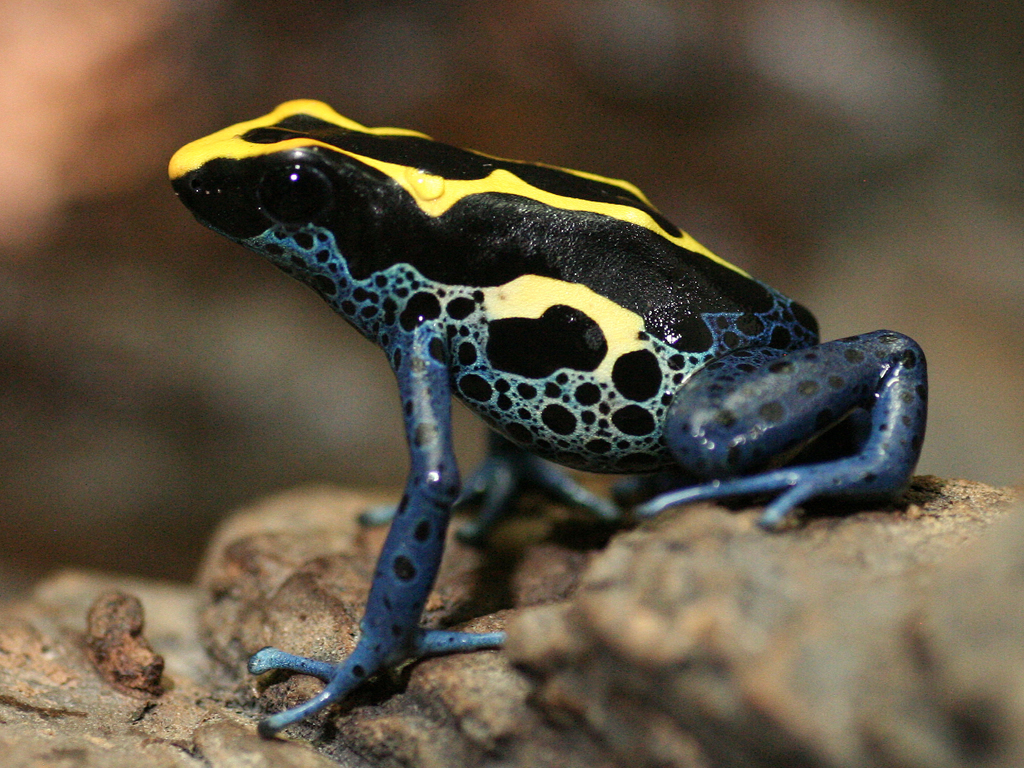

Photo: Sindy-Nero-CC-BY-NC
The females are larger
Like other frog species, the blue poison dart frog absorbs moisture through its skin and can also breathe through it. It has small discs on its feet that allows it to climb on leaves and branches. The frog has territories which it defends with loud calls. It can become aggressive both towards members of its own species and towards other animals.
Females of both the dyeing poison dart frog and the blue poison dart frog subspecies are larger than males. Males attract females in spring with special calls, and many females gather around them. The females then fight over who will get the most attractive male. After mating, the female lays a large quantity of eggs in shallow water, which are guarded by the parents.
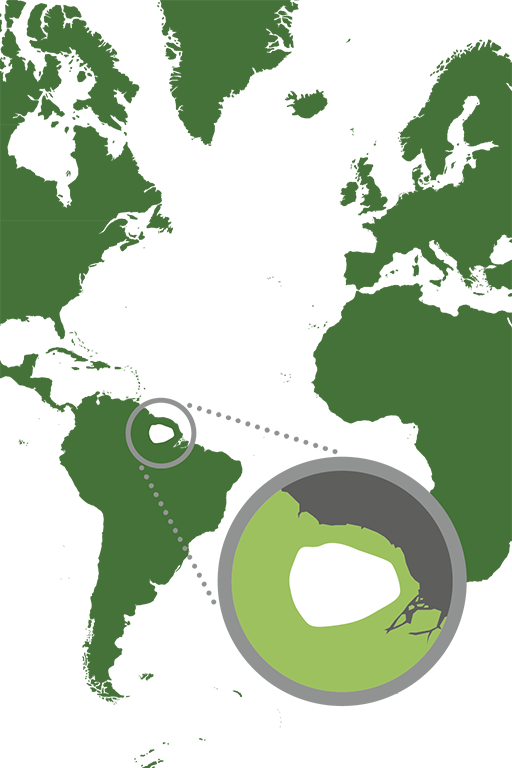
Distribution worldwide
South America, mainly Suriname.
White marking = Distribution
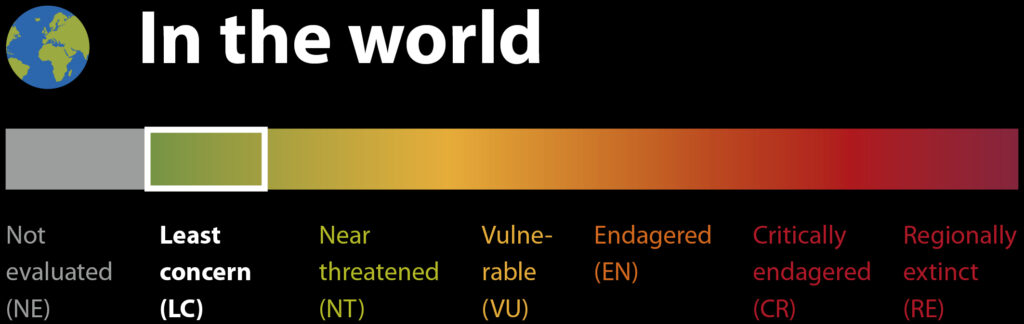
Threat based on the Red List
Trade regulations
CITES: B-listed.